Understanding Pakistan’s Rank 99 on the Global Hunger Index: Challenges and Path to Progress
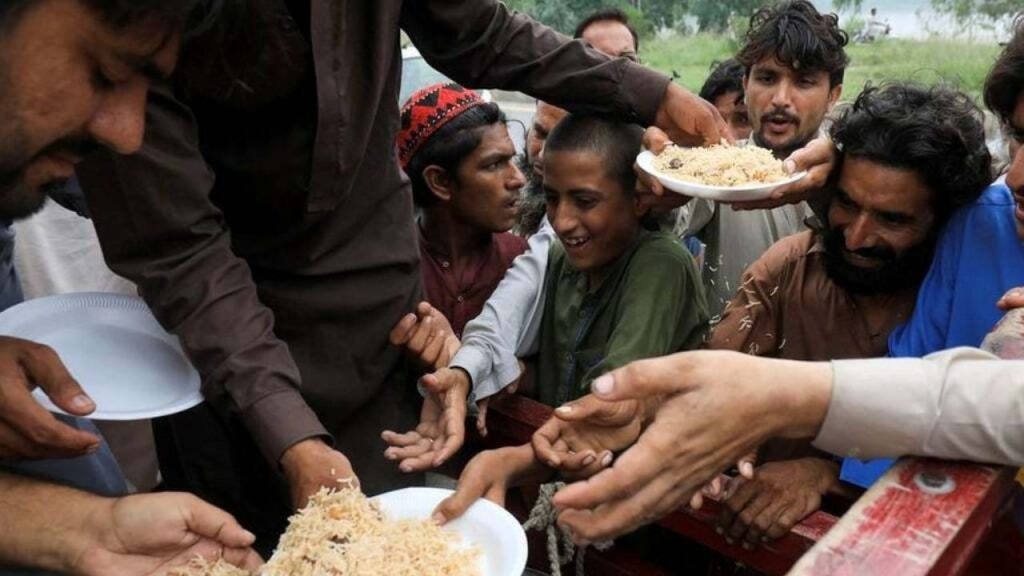

Understanding Pakistan's Rank 99 on the Global Hunger Index Challenges and Path to Progress
Introduction:
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) has a notable impact on the assessment and ranking of countries based on their hunger and malnutrition levels. countries according to the extent of hunger and malnutrition prevalent within their populations. Unfortunately, Pakistan finds itself at a concerning position, ranked 99th on the Global Hunger Index.
This ranking sheds light on the prevailing food insecurity and nutritional challenges faced by the nation. In this blog, we will delve into the key factors contributing to Pakistan’s low GHI score, explore the implications of hunger and malnutrition, and discuss potential strategies to improve the situation and pave the way towards a hunger-free nation.
Understanding the Global Hunger Index (GHI):
The Global Hunger Index is a multidimensional tool that assesses a country’s hunger situation based on four key indicators: undernourishment, child wasting, child stunting, and child mortality. Each factor represents a different aspect of malnutrition, offering a comprehensive view of a nation’s food security and nutrition status.
Causes of Hunger and Malnutrition in Pakistan:
- Poverty: High levels of poverty in Pakistan directly correlate with food insecurity. A significant portion of the population struggles to access adequate and nutritious food due to financial constraints.
- Water Scarcity: Pakistan faces water scarcity, affecting agricultural productivity and ultimately leading to reduced food production.
- Unstable Agricultural Practices: Limited technology adoption and inadequate infrastructure hinder agricultural growth, impacting food availability and affordability.
- Rapid Population Growth: Pakistan’s growing population adds pressure to the existing resources, making it challenging to meet the increasing food demands.
- Climate Change: Erratic weather patterns and natural disasters disrupt food production and lead to crop losses, exacerbating food insecurity.
Consequences of Hunger and Malnutrition:
- Impaired Physical Growth: Malnourished children experience stunted growth, leading to physical and cognitive developmental delays.
- Health Issues: Hunger weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to diseases and infections.
- Reduced Economic Productivity: Malnourished individuals are less productive, impacting the overall economic growth of the nation.
- Education Challenges: Malnutrition affects children’s learning abilities and school attendance, hindering their educational progress.
Government Initiatives and Challenges:
The Pakistani government has launched various initiatives to combat hunger and malnutrition, such as the Zero Hunger Program and the National Food Security Policy. Nevertheless, various obstacles continue to exist, such as:
- Funding Constraints: Limited financial resources hinder the implementation of comprehensive programs and projects.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient awareness about proper nutrition and its importance contributes to malnutrition rates.
- Distribution Inefficiencies: Inadequate distribution systems result in food wastage and hinder reaching vulnerable populations.
Promising Strategies for Improvement:
- Agricultural Reforms: Investing in modern agricultural techniques, water management, and infrastructure can enhance food production and food security.
- Social Safety Nets: Implementing social welfare programs like cash transfers and food vouchers can alleviate immediate hunger concerns for the most vulnerable.
- Nutrition Education: Raising awareness about proper nutrition and hygiene practices can lead to healthier dietary habits.
- Empowering Women: Empowering women through education and employment opportunities can positively impact household food security.
Partnerships involving both the public and private sectors:
Collaboration between the government, private sector, and non-governmental organizations is vital for comprehensive and sustainable solutions. Public-private partnerships can combine resources, expertise, and networks to tackle the complex issue of hunger and malnutrition.
International Aid and Support:
International organizations and donor countries can play a significant role in supporting Pakistan’s efforts to combat hunger. Foreign aid, technical assistance, and knowledge-sharing can amplify the impact of local initiatives.
Conclusion:
Pakistan’s ranking of 99th on the Global Hunger Index highlights the urgent need to address food insecurity and malnutrition within the country. By understanding the root causes and consequences of hunger, implementing effective government policies, promoting public awareness, and fostering collaborations between various stakeholders, Pakistan can make significant strides towards a hunger-free future. Together, we can work towards building a nation where every individual has access to sufficient and nutritious food, fostering a healthier, more productive, and prosperous society for generations to come.
For More Related Articles Browse Our Website Blogster.pk
For social Connection You can also Visit and follow our Social media Platforms
Facebook , Instagram, Linkedin, Pinterest, Quora, Twitter, Youtube.